Heat Shock Protein 72 Enhances Autophagy as a Protective Mechanism in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Peritonitis in Rats - The American Journal of Pathology

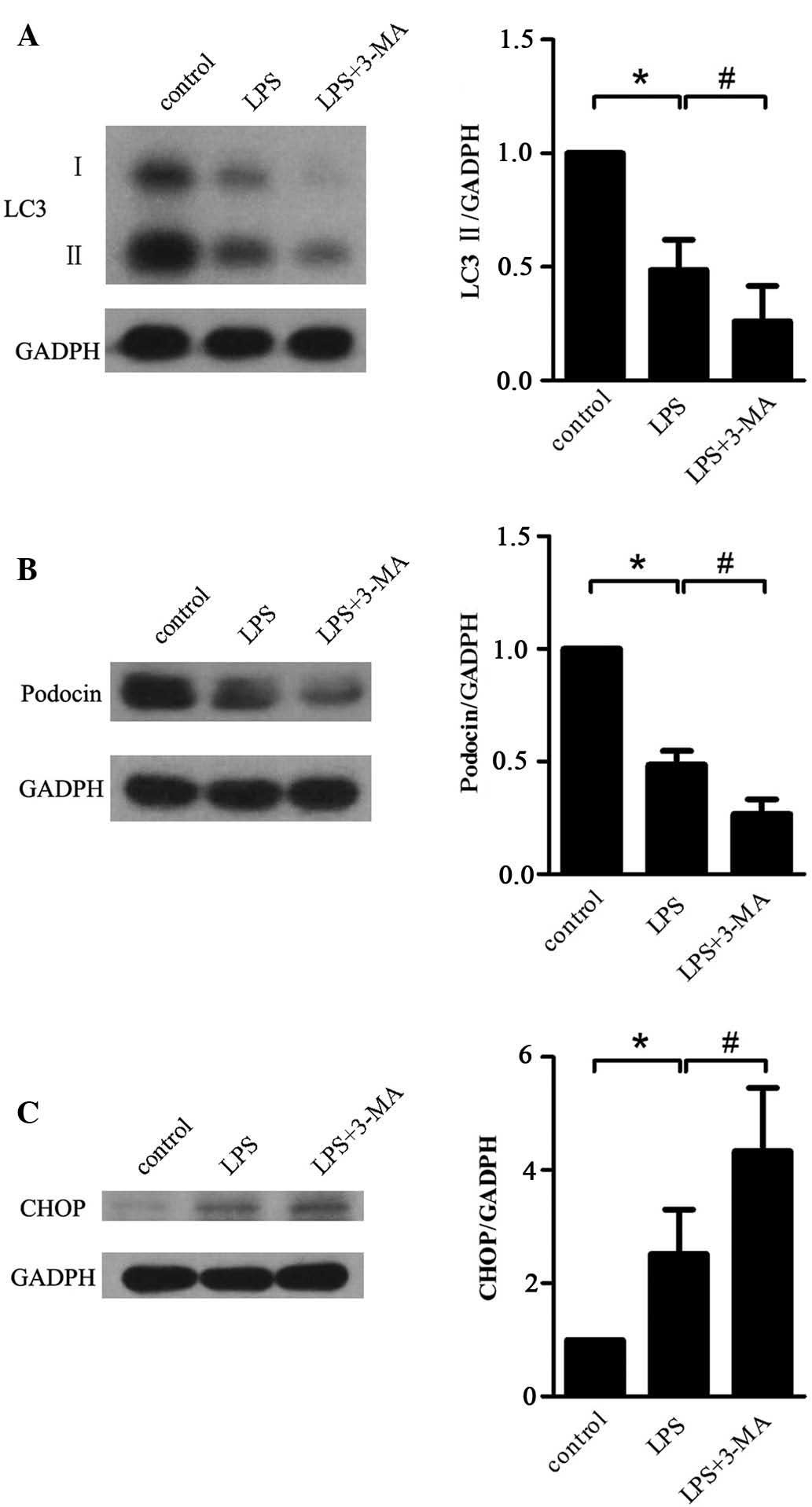
Prevention of D-GalN/LPS-induced ALI by 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid through PXR-mediated inhibition of autophagy degradation | Cell Death & Disease

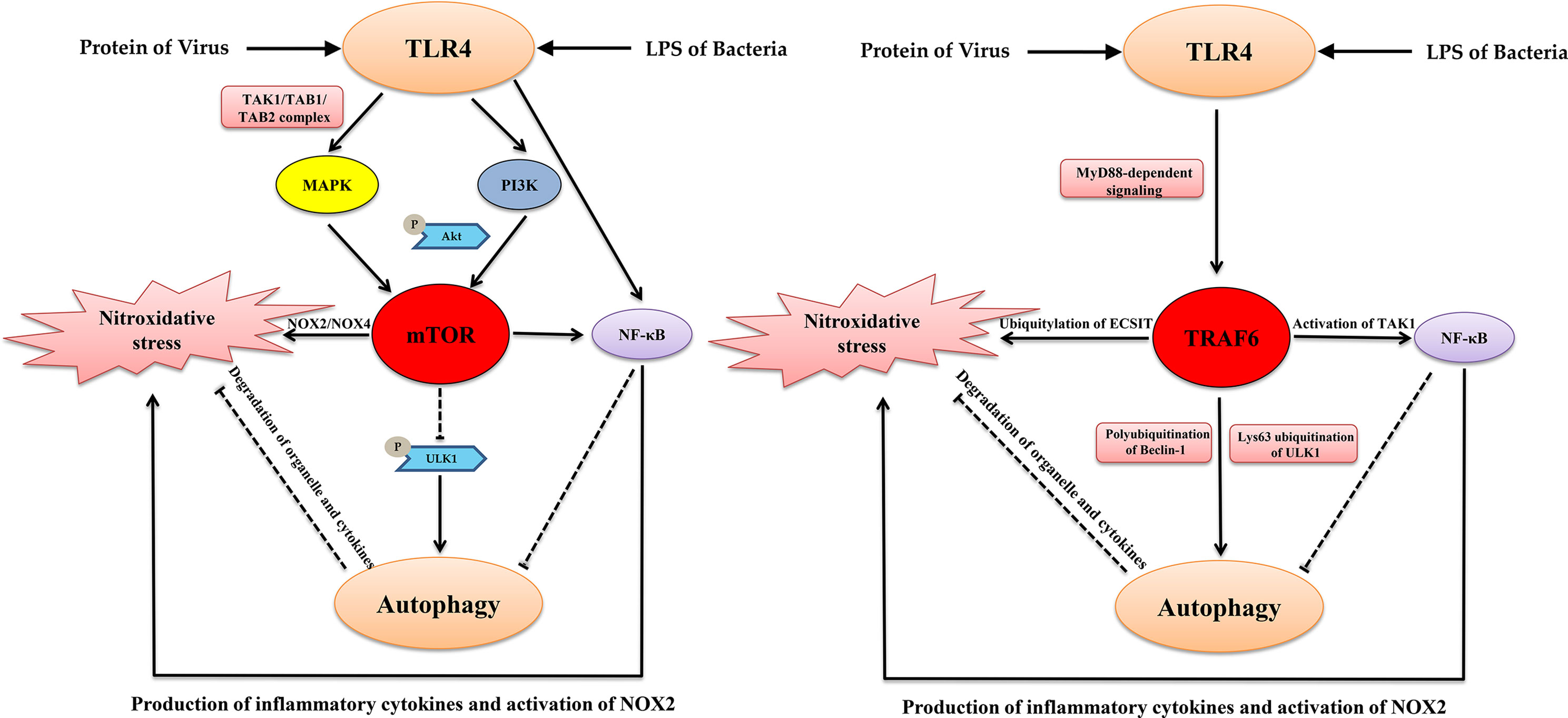
LPS-induced autophagy is mediated by oxidative signaling in cardiomyocytes and is associated with cytoprotection | American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced autophagy is involved in the restriction of Escherichia coliin peritoneal mesothelial cells | BMC Microbiology | Full Text
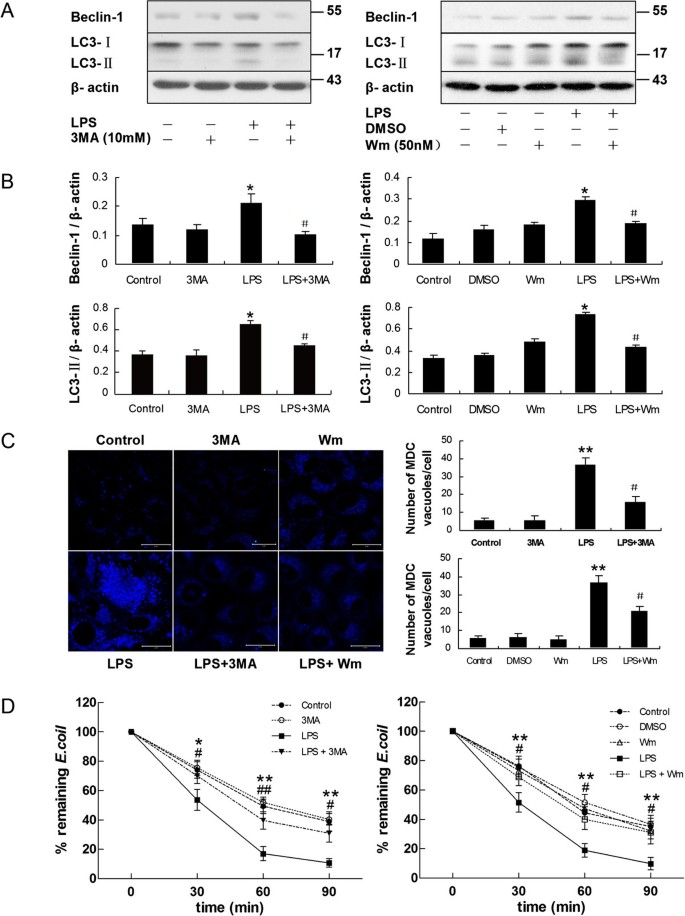
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced autophagy is involved in the restriction of Escherichia coliin peritoneal mesothelial cells | BMC Microbiology | Full Text

Artesunate reverses LPS tolerance by promoting ULK1-mediated autophagy through interference with the CaMKII-IP3R-CaMKKβ pathway - ScienceDirect
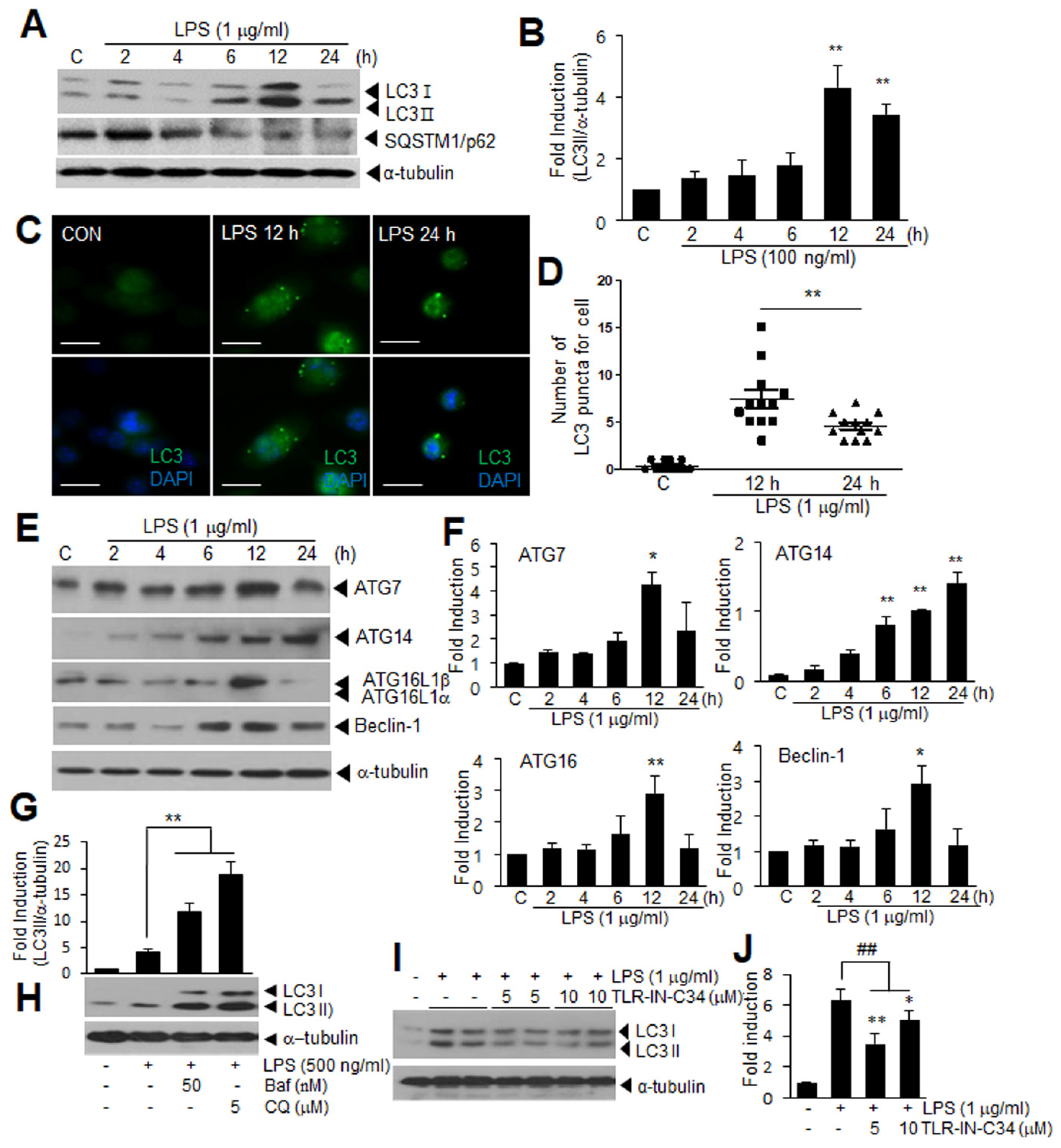
Cells | Free Full-Text | Cytosolic HMGB1 Mediates LPS-Induced Autophagy in Microglia by Interacting with NOD2 and Suppresses Its Proinflammatory Function | HTML
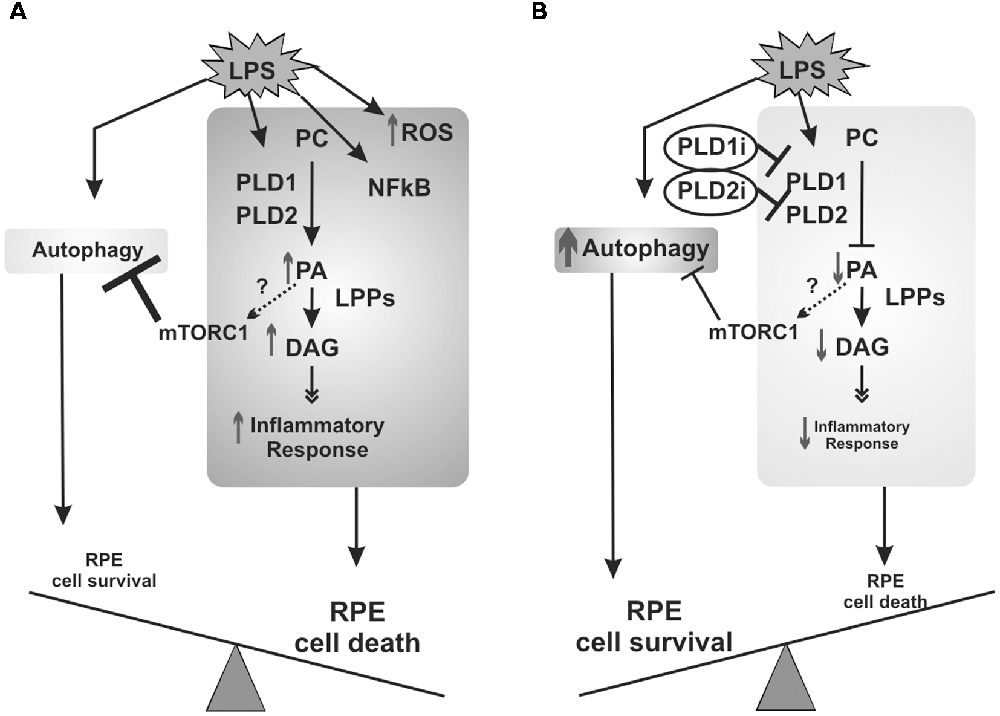
Frontiers | Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Autophagy Mediates Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cells Survival. Modulation by the Phospholipase D Pathway
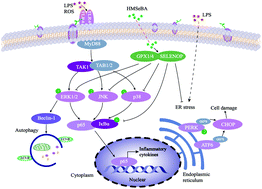
Maternal organic selenium supplementation alleviates LPS induced inflammation, autophagy and ER stress in the thymus and spleen of offspring piglets by improving the expression of selenoproteins - Food & Function (RSC Publishing)

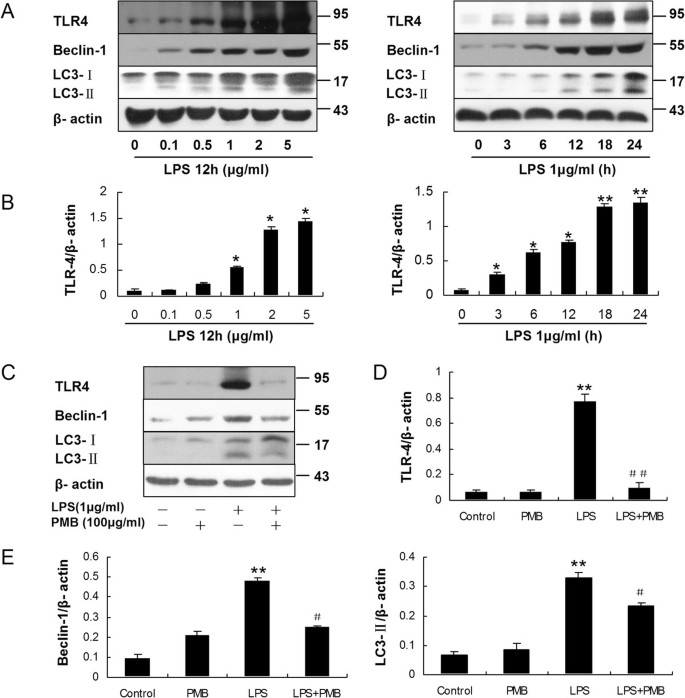
Nrf2-mediated induction of p62 controls Toll-like receptor-4–driven aggresome-like induced structure formation and autophagic degradation | PNAS
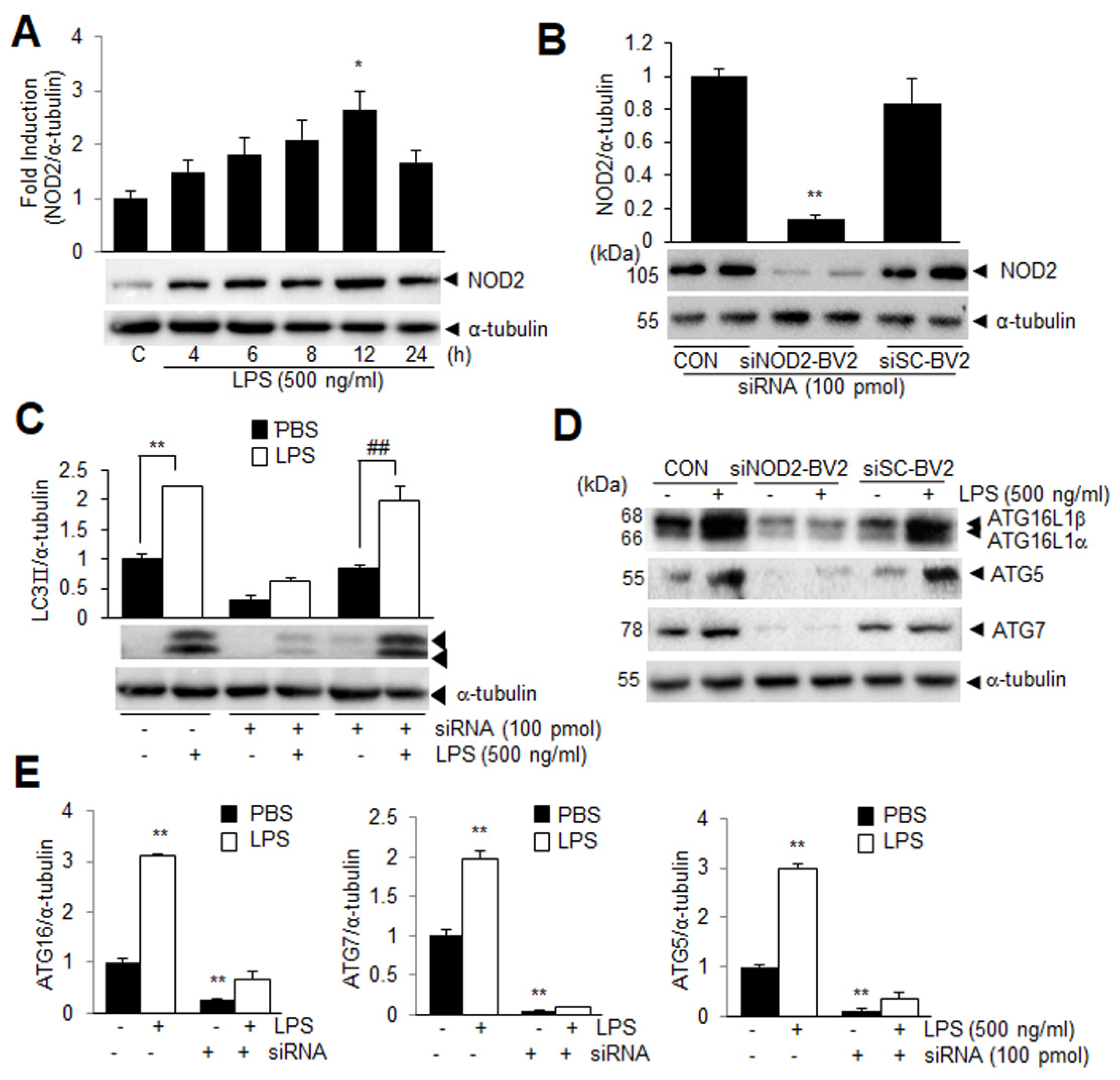
Cells | Free Full-Text | Cytosolic HMGB1 Mediates LPS-Induced Autophagy in Microglia by Interacting with NOD2 and Suppresses Its Proinflammatory Function | HTML

Figure 4 | GSTP1 Inhibits LPS-Induced Inflammatory Response Through Regulating Autophagy in THP-1 Cells | SpringerLink

LPS-induced autophagy is mediated by oxidative signaling in cardiomyocytes and is associated with cytoprotection | American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology
Autophagy Limits Endotoxemic Acute Kidney Injury and Alters Renal Tubular Epithelial Cell Cytokine Expression | PLOS ONE
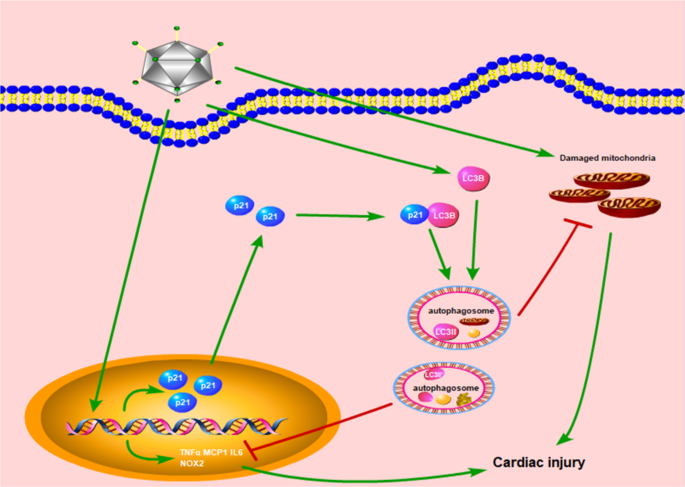
Autophagy is involved in the protective effect of p21 on LPS-induced cardiac dysfunction | Cell Death & Disease
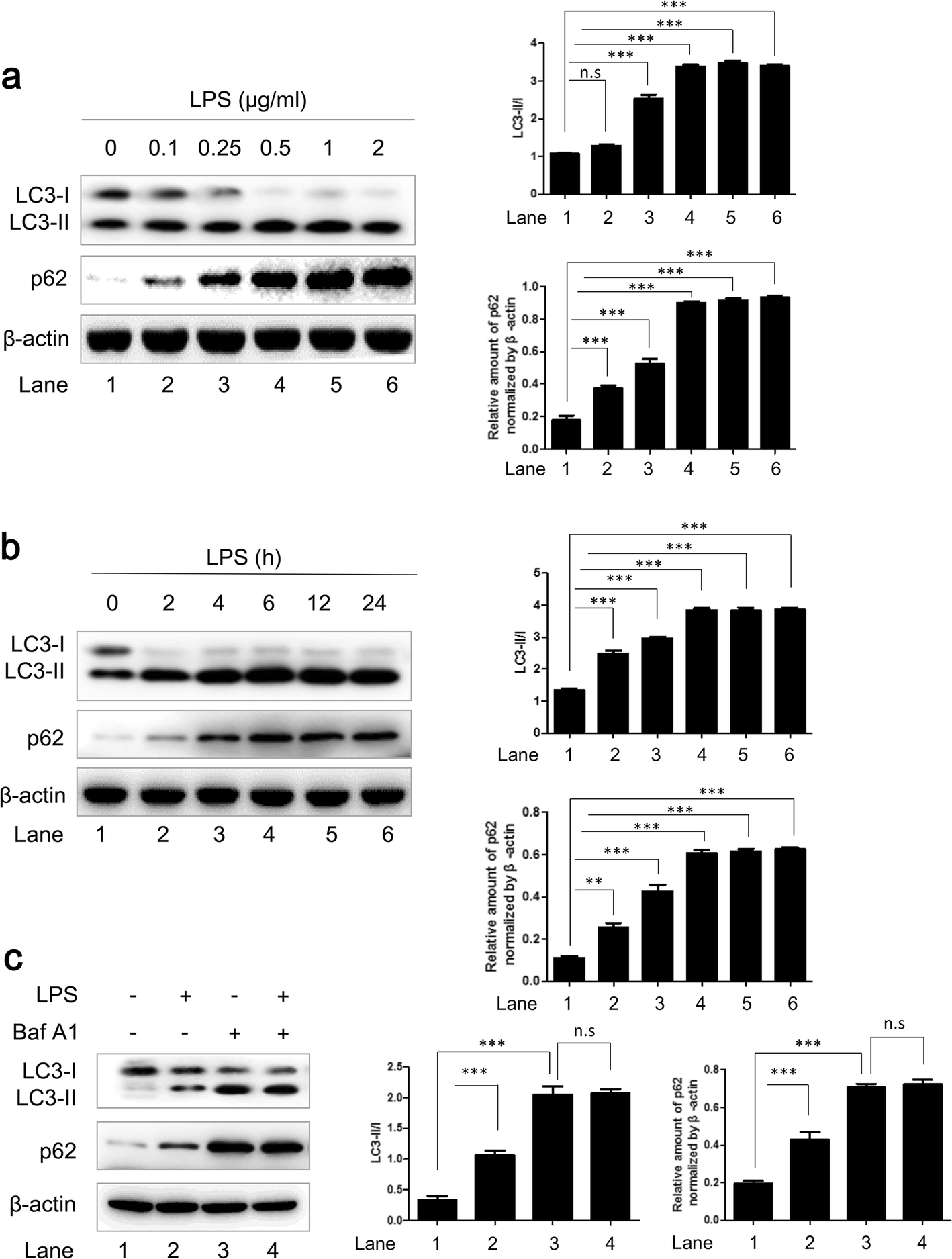
Figure 1 | GSTP1 Inhibits LPS-Induced Inflammatory Response Through Regulating Autophagy in THP-1 Cells | SpringerLink

Glycyrrhizic acid ameliorates LPS-induced acute lung injury by regulating autophagy through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. - Abstract - Europe PMC

LPS triggers mTOR phosphorylation and blocks autophagic flux in Caco-2... | Download Scientific Diagram

Autophagy Regulates IL-23 Secretion and Innate T Cell Responses through Effects on IL-1 Secretion | The Journal of Immunology